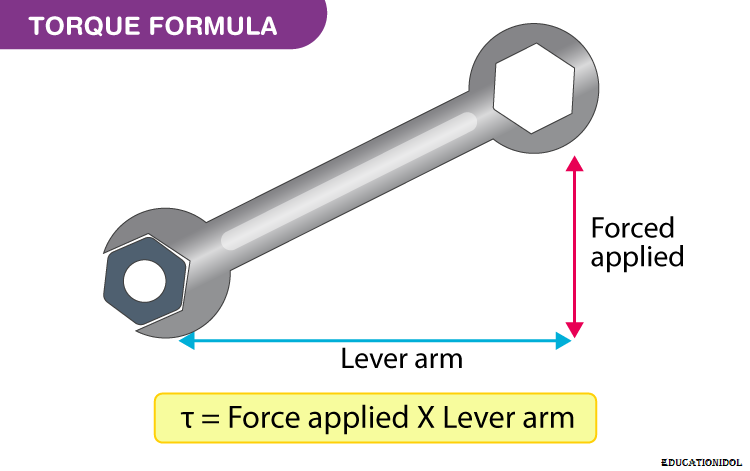
Torque is described as the turning effect of force on the axis of rotation. In brief, it is a moment of force. It is characterized by τ.
Torque formula is articulated as
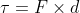
Where,
Force applied = F
From the axis of rotation the perpendicular distance of force = d
The Magnitude of torque is articulated as

Where θ is the angle between the force applied and the axis of rotation.
The SI unit for torque is Newton-meter (Nm).
Torque Solved Examples
Problem 1: The width of a door is 40 cm. If it is released by exerting a force of 2 N at its edge (away from the hinges).Compute the torque produced which causes the door to open.
Answer:
Force applied = F = 2 N
Length of lever arm = d = 40 cm
Torque = 0.40 m (as distance amid the line of action of force and axis of rotation is 40 cm)
Torque = F × d
= 0.40 × 20
Torque = 8 Nm.
Problem 2: The Classroom door is of width 50 cm. If the Handle of the door is 20 cm from the edge and the Force of 5 N is applied on the handle. Compute the torque.
Answer:
The handle of the door is located at 20 cm. Thus, the line of action is 20/2 = 10 cm.
Measurement of the lever arm = d = 50 – 10 = 40 cm = 0.4 m
Force exerted = 2N
Torque = F × d
= 2 × 0.4
Torque = 0.8 Nm.