Home / NCERT Solution / NCERT Solution for Class 10 / NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics
CBSE Board NCERT Solutions for Class 10th Mathematics Chapter 9 :Some Applications of Trigonometry
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class Ten Mathematics Chapter 9 -Some Applications of Trigonometry
NCERT Solutins For Class 10 Mathematics. Exercise 9.1
NCERT Solutions for Class X Maths Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry – Mathematics CBSE
Excercise: 9.1
Page No: 203
1. A circus artist is climbing a 20 m long rope, which is tightly stretched and tied from the top of a vertical pole to the ground. Find the height of the pole, if the angle made by the rope with the ground level is 30° (see Fig. 9.11).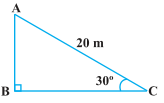
Answer :
Let AB be the vertical pole Ac be 20 m long rope tied to point C.
In right ΔABC,
sin 30° = AB/AC
⇒ 1/2 = AB/20
⇒ AB = 20/2
⇒ AB = 10
The height of the pole is 10 m.
2. A tree breaks due to storm and the broken part bends so that the top of the tree touches the ground making an angle 30° with it. The distance between the foot of the tree to the point where the top touches the ground is 8 m. Find the height of the tree.
Answer :
Let AC be the broken part of the tree.
∴ Total height of the tree = AB+AC
In right ΔABC,
cos 30° = BC/AC
⇒ √3/2 = 8/AC
⇒ AC = 16/√3
Also,
tan 30° = AB/BC
⇒ 1/√3 = AB/8
⇒ AB = 8/√3
Total height of the tree = AB+AC = 16/√3 + 8/√3 = 24/√3
3. A contractor plans to install two slides for the children to play in a park. For the children below the age of 5 years, she prefers to have a slide whose top is at a height of 1.5 m, and is inclined at an angle of 30° to the ground, whereas for elder children, she wants to have a steep slide at a height of 3 m, and inclined at an angle of 60° to the ground. What should be the length of the slide in each case?
Answer :
There are two slides of height 1.5 m and 3 m. (Given)
Let AB is 1.5 m and PQ be 3 m slides.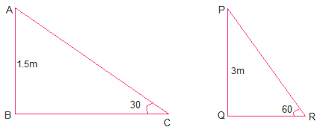
ABC is the slide inclined at 30° with length AC and PQR is the slide inclined at
60° with length PR.
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
sin 30° = AB/AC
⇒ 1/2 = 1.5/AC
⇒ AC = 3m
also,
In right ΔPQR,
sin 60° = PQ/PR
⇒ √3/2 = 3/PR
⇒ PR = 2√3 m
Hence, length of the slides are 3 m and 2√3 m respectively.
Page No: 204
4. The angle of elevation of the top of a tower from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the foot of the tower, is 30°. Find the height of the tower.
Answer :
Let AB be the height of the tower and C is the point elevation which is 30 m away from the foot of the tower.
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
tan 30° = AB/BC
⇒ 1/√3 = AB/30
⇒ AB = 10√3
Thus, the height of the tower is 10√3 m.
5. A kite is flying at a height of 60 m above the ground. The string attached to the kite is temporarily tied to a point on the ground. The inclination of the string with the ground is 60°. Find the length of the string, assuming that there is no slack in the string.
Answer :
Let BC be the height of the kite from the ground,
AC be the inclined length of the string from the ground and A is the point where string of the kite is tied.
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
sin 60° = BC/AC
⇒ √3/2 = 60/AC
⇒ AC = 40√3 m
Thus, the length of the string from the ground is 40√3 m.
6. A 1.5 m tall boy is standing at some distance from a 30 m tall building. The angle of elevation from his eyes to the top of the building increases from 30° to 60° as he walks towards the building. Find the distance he walked towards the building.
Answer :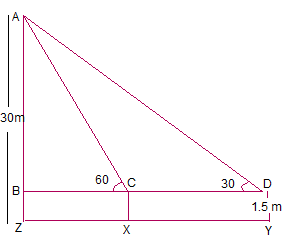
Let the boy initially standing at point Y with inclination 30° and then he approaches the building to
the point X with inclination 60°.
∴ XY is the distance he walked towards the building.
also, XY = CD.
Height of the building = AZ = 30 m
AB = AZ – BZ = (30 – 1.5) = 28.5 m
A/q,
In right ΔABD,
tan 30° = AB/BD
⇒ 1/√3 = 28.5/BD
⇒ BD = 28.5√3 m
also,
In right ΔABC,
tan 60° = AB/BC
⇒ √3 = 28.5/BC
⇒ BC = 28.5/√3 = 28.5√3/3 m
∴ XY = CD = BD – BC = (28.5√3 – 28.5√3/3) = 28.5√3(1-1/3) = 28.5√3 × 2/3 = 57/√3 m.
Thus, the distance boy walked towards the building is 57/√3 m.
7. From a point on the ground, the angles of elevation of the bottom and the top of a transmission tower fixed at the top of a 20 m high building are 45° and 60° respectively. Find the height of the tower.
Answer :
Let BC be the 20 m high building.
D is the point on the ground from where the elevation is taken.
Height of transmission tower = AB = AC – BC
A/q,
In right ΔBCD,
tan 45° = BC/CD
⇒ 1 = 20/CD
⇒ CD = 20 m
also,
In right ΔACD,
tan 60° = AC/CD
⇒ √3 = AC/20
⇒ AC = 20√3 m
Height of transmission tower = AB = AC – BC = (20√3 – 20) m = 20(√3 – 1) m.
8. A statue, 1.6 m tall, stands on the top of a pedestal. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the statue is 60° and from the same point the angle of elevation of the top of the pedestal is 45°. Find the height of the pedestal.
Answer :
Let AB be the height of statue.
D is the point on the ground from where the elevation is taken.
Height of pedestal = BC = AC – AB
A/q,
In right ΔBCD,
tan 45° = BC/CD
⇒ 1 = BC/CD
⇒ BC = CD.
also,
In right ΔACD,
tan 60° = AC/CD
⇒ √3 = AB+BC/CD
⇒ √3CD = 1.6 m + BC
⇒ √3BC = 1.6 m + BC
⇒ √3BC – BC = 1.6 m
⇒ BC(√3-1) = 1.6 m
⇒ BC = 1.6/(√3-1) m
⇒ BC = 0.8(√3+1) m
Thus, the height of the pedestal is 0.8(√3+1) m.
9. The angle of elevation of the top of a building from the foot of the tower is 30° and the angle of elevation of the top of the tower from the foot of the building is 60°. If the tower is 50 m high, find the height of the building.
Answer :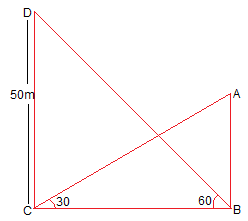
Let CD be the height of the tower equal to 50 m (Given)
Let AB be the height of the building.
BC be the distance between the foots of the building and the tower.
Elevation is 30° and 60° from the tower and the building respectively.
A/q,
In right ΔBCD,
tan 60° = CD/BC
⇒ √3 = 50/BC
⇒ BC = 50/√3
also,
In right ΔABC,
tan 30° = AB/BC
⇒ 1/√3 = AB/BC
⇒ AB = 50/3
Thus, the height of the building is 50/3.
10. Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite each other on either side of the road, which is 80 m wide. From a point between them on the road, the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60° and 30°, respectively. Find the height of the poles and the distances of the point from the poles.
Answer :
Let AB and CD be the poles of equal height.
O is the point between them from where the height of elevation taken.
BD is the distance between the poles.
A/q,
AB = CD,
OB + OD = 80 m
Now,
In right ΔCDO,
tan 30° = CD/OD
⇒ 1/√3 = CD/OD
⇒ CD = OD/√3 … (i)
also,
In right ΔABO,
tan 60° = AB/OB
⇒ √3 = AB/(80-OD)
⇒ AB = √3(80-OD)
AB = CD (Given)
⇒ √3(80-OD) = OD/√3
⇒ 3(80-OD) = OD
⇒ 240 – 3 OD = OD
⇒ 4 OD = 240
⇒ OD = 60
Putting the value of OD in equation (i)
CD = OD/√3 ⇒ CD = 60/√3 ⇒ CD = 20√3 m
also,
OB + OD = 80 m ⇒ OB = (80-60) m = 20 m
Thus, the height of the poles are 20√3 m and distance from the point of elevation are 20 m and 60 m respectively.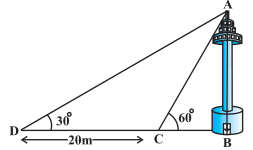
11. A TV tower stands vertically on a bank of a canal. From a point on the other bank directly opposite the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 60°. From another point 20 m away from this point on the line joining this point to the foot of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 30° (see Fig. 9.12). Find the height of the tower and the width of the canal.
Answer
Here, AB is the height of the tower.
CD = 20 m (given)
A/q,
In right ΔABD,
tan 30° = AB/BD
⇒ 1/√3 = AB/(20+BC)
⇒ AB = (20+BC)/√3 … (i)
also,
In right ΔABC,
tan 60° = AB/BC
⇒ √3 = AB/BC
⇒ AB = √3 BC … (ii)
From eqn (i) and (ii)
AB = √3 BC = (20+BC)/√3
⇒ 3 BC = 20 + BC
⇒ 2 BC = 20 ⇒ BC = 10 m
Putting the value of BC in eqn (ii)
AB = 10√3 m
Thus, the height of the tower 10√3 m and the width of the canal is 10 m.
12. From the top of a 7 m high building, the angle of elevation of the top of a cable tower is 60° and the angle of depression of its foot is 45°. Determine the height of the tower.
Answer :
Let AB be the building of height 7 m and EC be the height of tower.
A is the point from where elevation of tower is 60° and the angle of depression of its foot is 45°
EC = DE + CD
also, CD = AB = 7 m.
and BC = AD
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
tan 45° = AB/BC
⇒ 1= 7/BC
⇒ BC = 7 m = AD
also,
In right ΔADE,
tan 60° = DE/AD
⇒ √3 = DE/7
⇒ DE = 7√3 m
Height of the tower = EC = DE + CD
= (7√3 + 7) m = 7(√3+1) m.
13. As observed from the top of a 75 m high lighthouse from the sea-level, the angles of depression of two ships are 30° and 45°. If one ship is exactly behind the other on the same side of the lighthouse, find the distance between the two ships.
Answer: 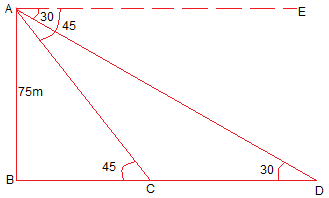
Let AB be the lighthouse of height 75 m.
Let C and D be the positions of the ships.
30° and 45° are the angles of depression from the lighthouse.
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
tan 45° = AB/BC
⇒ 1= 75/BC
⇒ BC = 75 m
also,
In right ΔABD,
tan 30° = AB/BD
⇒ 1/√3 = 75/BD
⇒ BD = 75√3 m
The distance between the two ships = CD = BD – BC = (75√3 – 75) m = 75(√3-1) m.
Page No: 205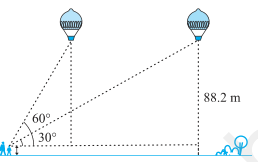
14. A 1.2 m tall girl spots a balloon moving with the wind in a horizontal line at a height of 88.2 m
from the ground. The height of 88.2 m from the ground. The angle of elevation of the balloon from the eyes of the girl at any instant is 60°. After some time, the angle of elevation reduces to 30° (see Fig. 9.13). Find the distance travelled by the balloon during the interval.
Answer :
Let the initial position of the balloon be A and final position be B.
Height of balloon above the girl height = 88.2 m – 1.2 m = 87 m
Distance travelled by the balloon =
DE = CE – CD
A/q,
In right ΔBEC,
tan 30° = BE/CE
⇒ 1/√3= 87/CE
⇒ CE = 87√3 m
also,
In right ΔADC,
tan 60° = AD/CD
⇒ √3= 87/CD
⇒ CD = 87/√3 m = 29√3 m
Distance travelled by the balloon = DE = CE – CD = (87√3 – 29√3) m = 29√3(3 – 1) m = 58√3 m.
15. A straight highway leads to the foot of a tower. A man standing at the top of the tower observes a car at an angle of depression of 30°, which is approaching the foot of the tower with a uniform speed. Six seconds later, the angle of depression of the car is found to be 60°. Find the time taken by the car to reach the foot of the tower from this point.
Answer :
Let AB be the tower.
D is the initial and C is the final position of the car respectively.
Angles of depression are measured from A.
BC is the distance from the foot of the tower to the car.
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
tan 60° = AB/BC
⇒ √3 = AB/BC
⇒ BC = AB/√3 m
also,
In right ΔABD,
tan 30° = AB/BD
⇒ 1/√3 = AB/(BC + CD)
⇒ AB√3 = BC + CD
⇒ AB√3 = AB/√3 + CD
⇒ CD = AB√3 – AB/√3
⇒ CD = AB(√3 – 1/√3)
⇒ CD = 2AB/√3
Here, distance of BC is half of CD. Thus, the time taken is also half.
Time taken by car to travel distance CD = 6 sec.
Time taken by car to travel BC = 6/2 = 3 sec.
16. The angles of elevation of the top of a tower from two points at a distance of 4 m and 9 m from the base of the tower and in the same straight line with it are complementary. Prove that the height of the tower is 6 m.
Answer :
Let AB be the tower.
C and D be the two points with distance 4 m and 9 m from the base respectively.
A/q,
In right ΔABC,
tan x = AB/BC
⇒ tan x = AB/4
⇒ AB = 4 tan x … (i)
also,
In right ΔABD,
tan (90°-x) = AB/BD
⇒ cot x = AB/9
⇒ AB = 9 cot x … (ii)
Multiplying eqn (i) and (ii)
AB2 = 9 cot x × 4 tan x
⇒ AB2 = 36
⇒ AB = ± 6
Height cannot be negative. Therefore, the height of the tower is 6 m. Hence, Proved.
EducationIdol are provided study materials for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 9, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 9 revision notes, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 9 question papers, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 9 sample papers, NCERT solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 9 syllabus and NCERT solutions for Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 9 important questions. Students can prepare and score well using education idol study materials.