Cell is called the fundamental unit of life.
The word cell is derived from the Latin word “cellula” which means “a little room”.
A cell is capable of independent existence and can carry out all the functions which are necessary for a living being. A cell carries out nutrition, respiration, excretion, transportation and reproduction; the way an individual organism does. Unicellular organisms are capable of independent existence which shows a cell’s capability to exist independently. Due to this, a cell is called the fundamental and structural unit of life. All living beings are composed of the basic unit of life, i.e. cell.
CELL THEORY (Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow):
• All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
• The cell is the basic unit of structure, function, and organization in all organisms.
• All cells come from pre-existing, living cells.
STRUCTURE OF CELL
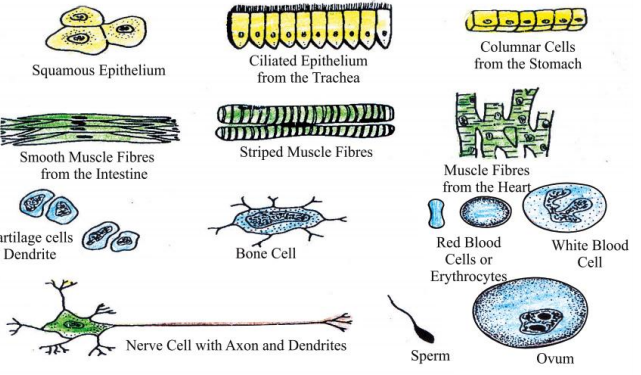
Shape and Size of Cells:- Cells come in all shapes and sizes. While most of the cells are spherical in shape, cells of various other shapes are also found. Most of the cells are microscopic in size, i.e. it is impossible to see them with naked eyes. Some cells are fairly large, e.g. a neuron in human body can be as long as 1 meter. The egg of an ostrich is the largest known cell of a living animal and an average egg is 15 cm long and 13 cm wide. Among the plants, the
largest cell is ovule of Cycas.
A cell is enclosed in a membranous casing and is filled with a liquid substance which is called the cytoplasm. There are many cell organelles in a typical cell. Some of the main structures of a cell are as follows: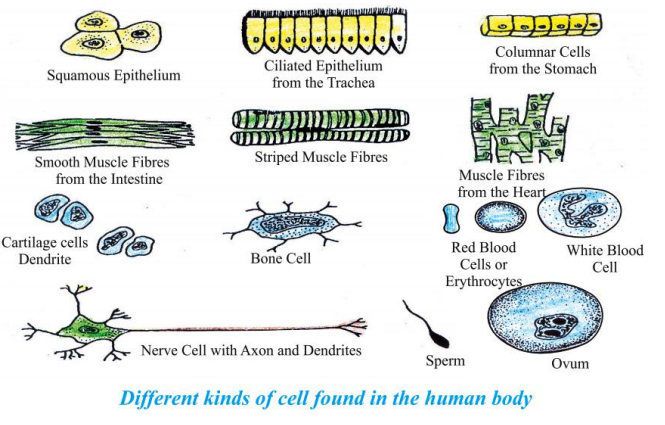
HISTORY OF DISCOVERY OF CELLS
• Robert Hooke was the first to discover cell (1665).
• Leeuwenhoek was the first to discover free living cells in pond water (1674).
• Robert Brown discovered the nucleus (1831).
• Purkinje coined the term ‘protoplasm (1839). Sr. SME Kuldeep Sharma ScienceZone(IXth)
• Schleiden (1838) and Schwann (1839) proposed the Cell Theory. Virchow (1855) made further addition to the cell
theory.
• The discovery of electron microscope (1940) made it possible to study the structures of cell organelles. The invention of magnifying lenses led to the discovery of the microscopic world. It is now known that a single cell may constitute a whole organism as in Amoeba, Chlamydomonas, Paramoecium and bacteria.
These organisms are called unicellular organisms (uni = single). On the other hand, many cells group together in a single body and assume different functions in it to form various body parts in multicellular organisms (multi = many) such as some fungi, plants and animals.
Cell wall: Cell wall is made of cellulose. It is somewhat hard but permeable to most of the substances. Cell wall is available in plant cells and in cells of bacteria and fungi.
Plasma membrane(Plasmalemma): Plasma membrane is a semi-permeable membrane. It is composed of bilayer of lipid and protein.
Functions of Plasma Membrane: Plasma membrane provides a container to the cytoplasm. It facilitates passage of various substances in and out of the cell.
Some substances like carbon dioxide or oxygen can move across the cell membrane by a process called diffusion. We saw that there is spontaneous movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region where its concentration is low.
Something similar to this happens in cells when, for example, some substance like CO2 (which is cellular waste and requires to be excreted out by the cell) accumulates in high concentrations inside the cell. In the cell’s external environment, the concentration of CO2 is low as compared to that inside the cell. As soon as there is a difference of concentration of CO2 inside and outside a cell, CO2 moves out of the cell, from a region of high concentration, to a
region of low concentration outside the cell by the process of diffusion. Similarly, O2 enters the cell by the process of diffusion when the level or concentration of O2 inside the cell decreases. Thus, diffusion plays an important role in gaseous exchange between the cells as well as the cell and its external environment.
Water also obeys the law of diffusion. The movement of water molecules through such a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. The movement of water across the plasma membrane is also affected by the amount of substance dissolved in water. Thus, osmosis is the passage of water from a region of high water concentration through a semi-permeable membrane to a region of low water concentration.
Plasma membrane helps in diffusion and osmosis.
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from high to regions of lower concentration as a result of random molecular motion. Diffusion tends to distribute molecules uniformly.
Exchange of gases like CO2 and O2 in lungs, plants, blood cells, O2 entering stomata of leaves are examples of diffusion.
Diffusion is passive transport i.e. no external energy is provided for the movement of molecules. The natural kinetic energy of the particle supplies the energy.
Osmosis
Osmosis is a special type of diffusion i.e. passage of water (solvent) across a selectively permeable membrane, from a region of high water concentration (dilute solution) to the region of low water concentration (concentrated solution).
Osmosis is also a passive transport i.e. no external energy is required for the passage.
There are two type of osmosis:
1. Endosmosis: The process in which the water molecules enter into the cell is known as endosmosis.
2. Exosmosis: The process in which the water molecules move out of the cell is known as exosmosis.