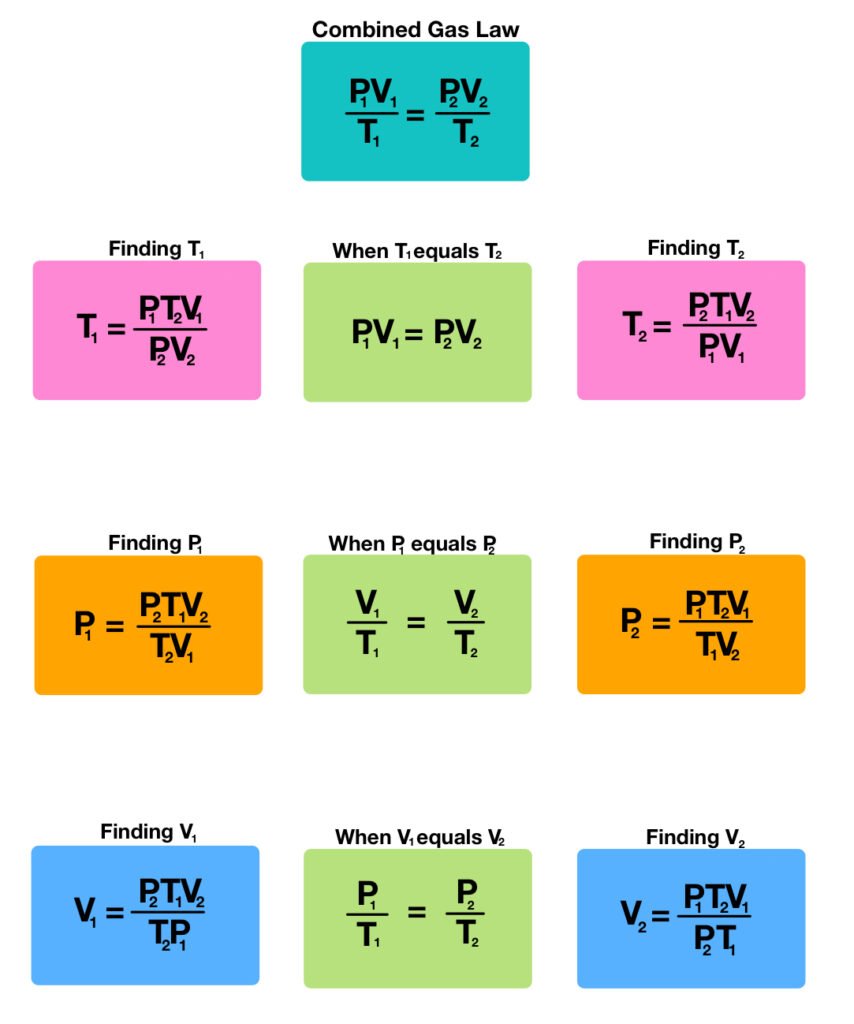
Combined gas law can be mathematically expressed as
k = PV/T
Where,
P = pressure
T = temperature in kelvin
V = volume
K = constant (units of energy divided by temperature)
When two substances are compared in two different conditions, the law can be stated as,
PiVi/Ti = PfVf/Tf
Where,
Pi = initial pressure
Vi = initial volume
Ti = initial temperature
Pf = final pressure
Vf= final volume
Tf = final temperature