Snell’s Law
Snell’s law is defined as “The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media”. Snell’s law formula is expressed as:
Where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction. This constant value is called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first.
The following is a diagrammatic representation:
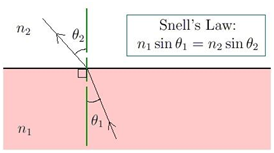
Snell’s Law Formula
Snell’s law formula is derived from Fermat’s principle. Fermat’s principle states that “light travels in the shortest path that takes the least time”.

This is the rendered form of the equation. You can not edit this directly. Right click will give you the option to save the image, and in most browsers you can drag the image onto your desktop or another program.
The normal on the surface is used to gauge the angles that the refracted ray creates at the contact point. n1 and n2 are the two different mediums that will impact the refraction.θ1 is the angle of incidence; θ2 is the angle of refraction.
Applications of Snell’s Law Formula in Real Life:
Snell’s law has a wide range of applications in physics especially in the branch of optics. It is used in optical apparatus such as eyeglasses, contact lenses, cameras, rainbows. There is an instrument called a refractometer that uses Snell’s law to calculate the refractive index of liquids. It is used all the time in the candy-making industry.