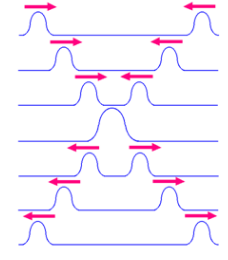
Principle of Superposition
The total current in any part of a linear circuit equals the algebraic sum of the currents produced by each source separately.
For example:
If the response produced by input A is X and that produced by input B is Y, then the response produced by input A+B is X+Y.